Hiring an ethical hacker is one way organisations can overcome skills gaps and time shortages - so what exactly can they bring to the table?
What are the biggest security risks of organisations, according to ethical hackers?
- Lack of in-house expertise (32%)
- lack of visibility into the attack surface (23%)
- insufficient deep testing (22%)
What do ethical hackers focus on?
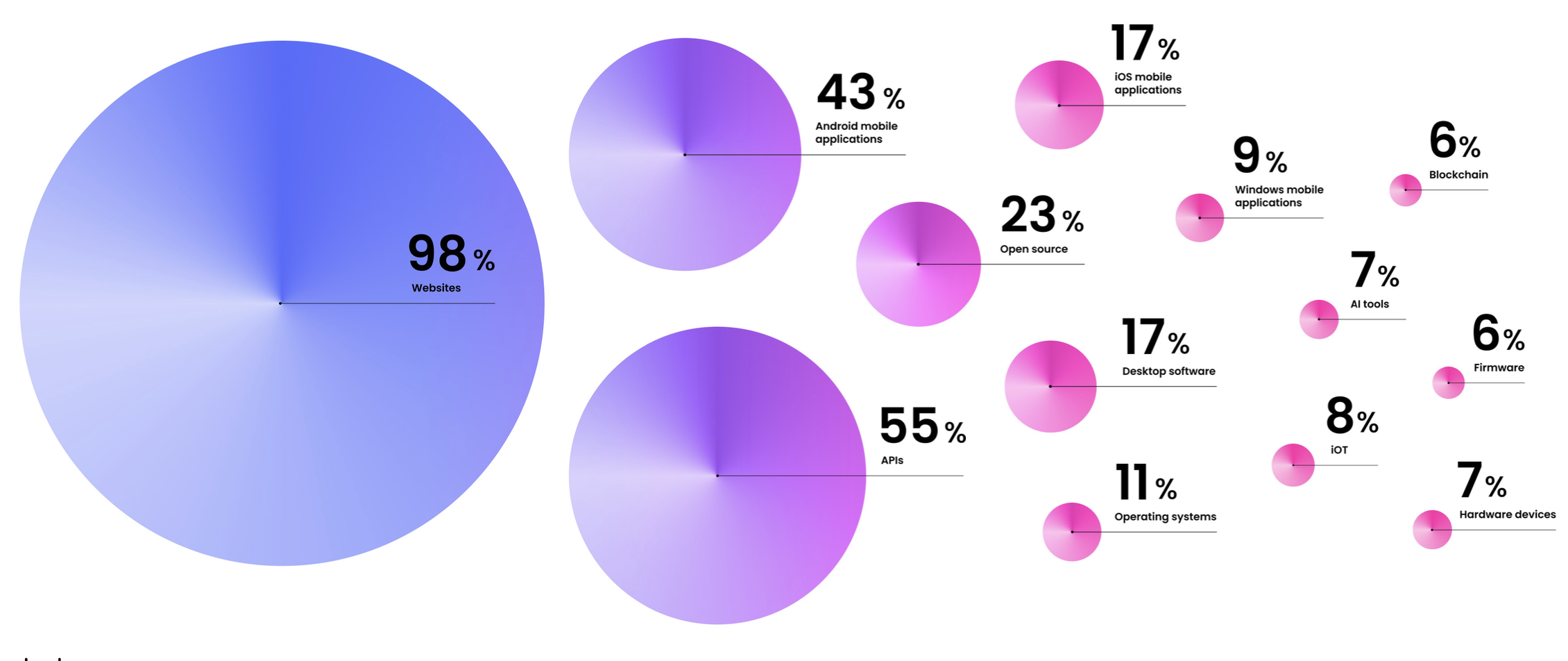
- Most ethical focus their efforts on websites (98%), followed by APIs (55%) and Android devices (43%)
- With only 17%, iOS receives relatively little attention. Eight percent specialise in IoT technology, and %7 of hackers now specialise in generative AI tools.
Source: 7th Annual Hacker-Powered Security Report - HackerOne
What motivates ethical hackers?
- Only one-quarter of hackers work full-time, and two-thirds of hackers work 20h or less. Many have a daytime job in the cybersecurity industry
- 80% of ethical hackers work for the financial reward, 78% say they do it to learn, and 47% do it to protect businesses
Why do ethical hackers choose a particular organisation?
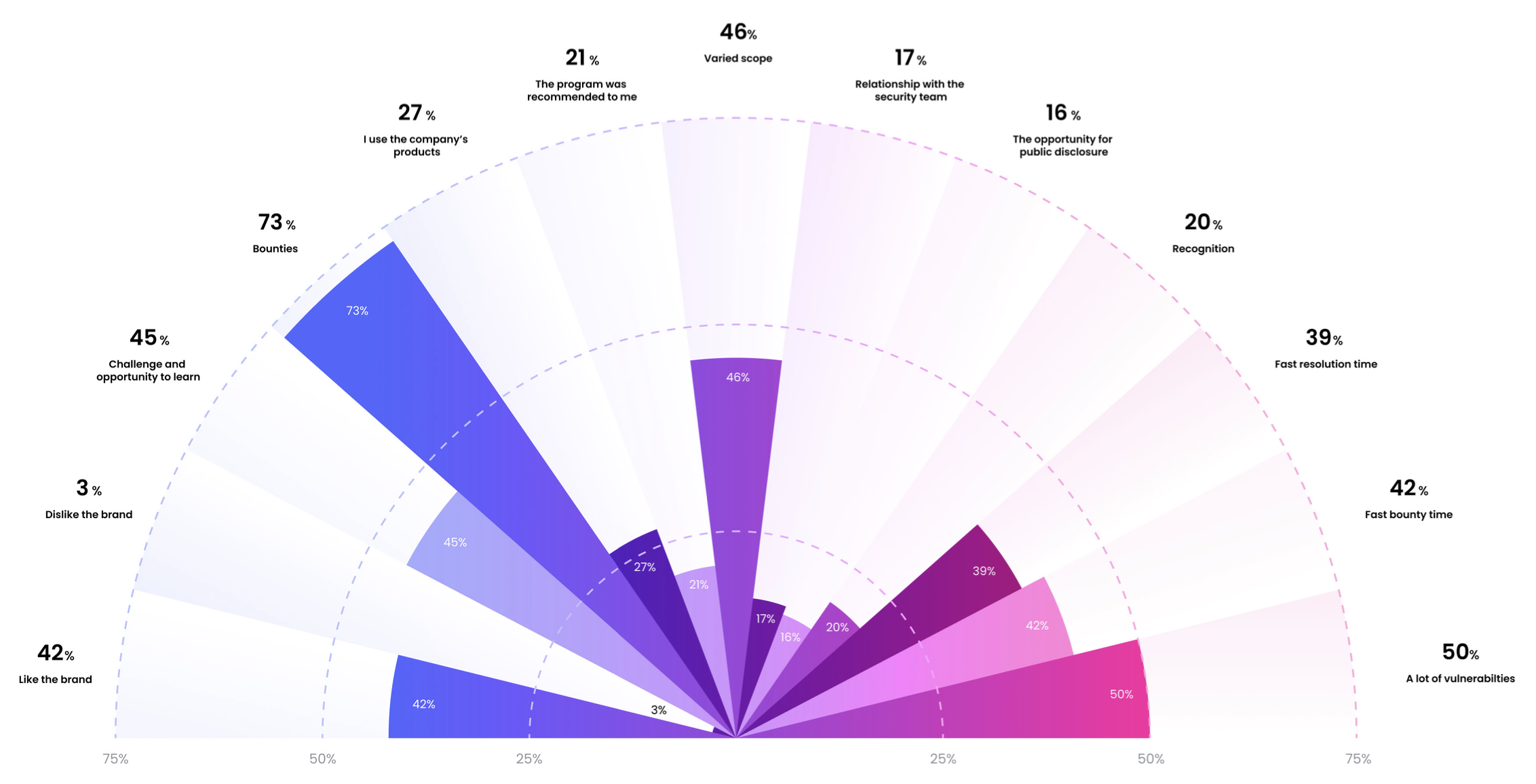
- A large bounty! 73% of attackers are looking for bounty money, followed by many vulnerabilities (50%) and an opportunity to learn (45%)
Source: 7th Annual Hacker-Powered Security Report - HackerOne
What are ethical hackers’ skill sets?
- Hackers’ skill sets include web penetration testing (95%), network penetration testing (47%), vulnerability research (63%), red team testing (20%), and social engineering testing (20%).
- Their biggest areas of specialisation are websites (98%), android mobile applications (43%), APIs (55%), and open source (23%).
What is the financial reward?
- On average, companies pay $1k for a bug disclosure. Companies in Crypto and blockchain lead the charge with an average payout of $6k, Travel & Hospitality as well as Computer software companies pay the lowest average reward ($1.5k)
A deep dive into GenAI:
- Now that artificial intelligence is ubiquitous, security leaders have two new challenges to contend with: harnessing GenAI, and protecting themselves from the threats it poses. It seems to be an even split:
- 55% of hackers say that generative AI tools will themselves become a major target for them.
- Similarly, 53% of ethical hackers are embedding GenAI into their processes to boost productivity.
- Hackers’ concerns about the risks posed by GenAI include that it will be exploited by criminals (28%), that it is a powerful tool for spreading disinformation (22%), and that it could spit out insecure code (18%).
- The top 10 vulnerabilities for large language models are:
- Prompt injection
- Insecure output handling
- Training data poisoning
- Model denial of service
- Supply chain vulnerabilities
- Sensitive information disclosure
- Insecure plugin design
- Excessive agency
- Overreliance
- Model theft






